Wonders never seize! When the Covid-19 pandemic made face masks an everyday essential, Japanese startup Donut Robotics spotted an opportunity. As people around the world are being urged to wear face masks when out in public, it hasn’t taken long for the functionality of a mask to be greatly enhanced but thanks to technology. The Donut Robotics has created a smart mask (C-Face smart mask) – a high-tech upgrade to standard face coverings, designed to make communication and social distancing easier through translations.
How the smart face mask works in conjunction with the translations world
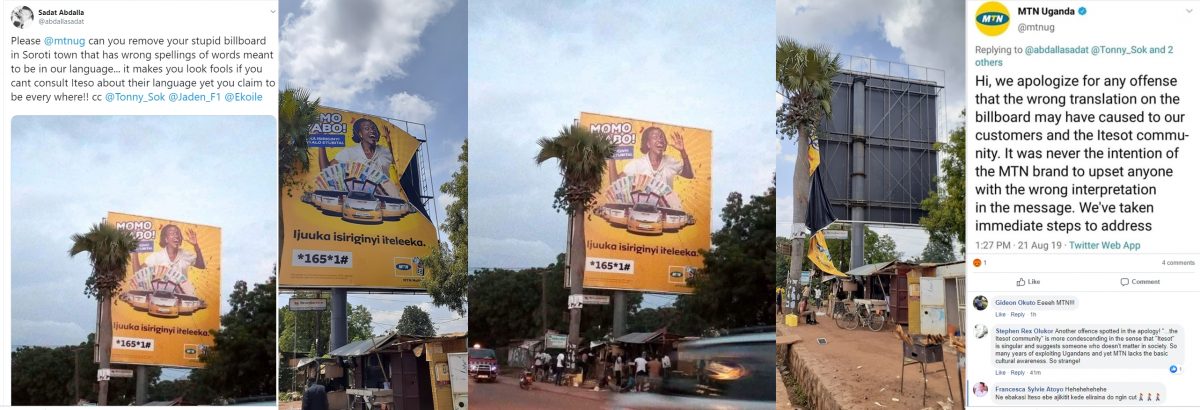
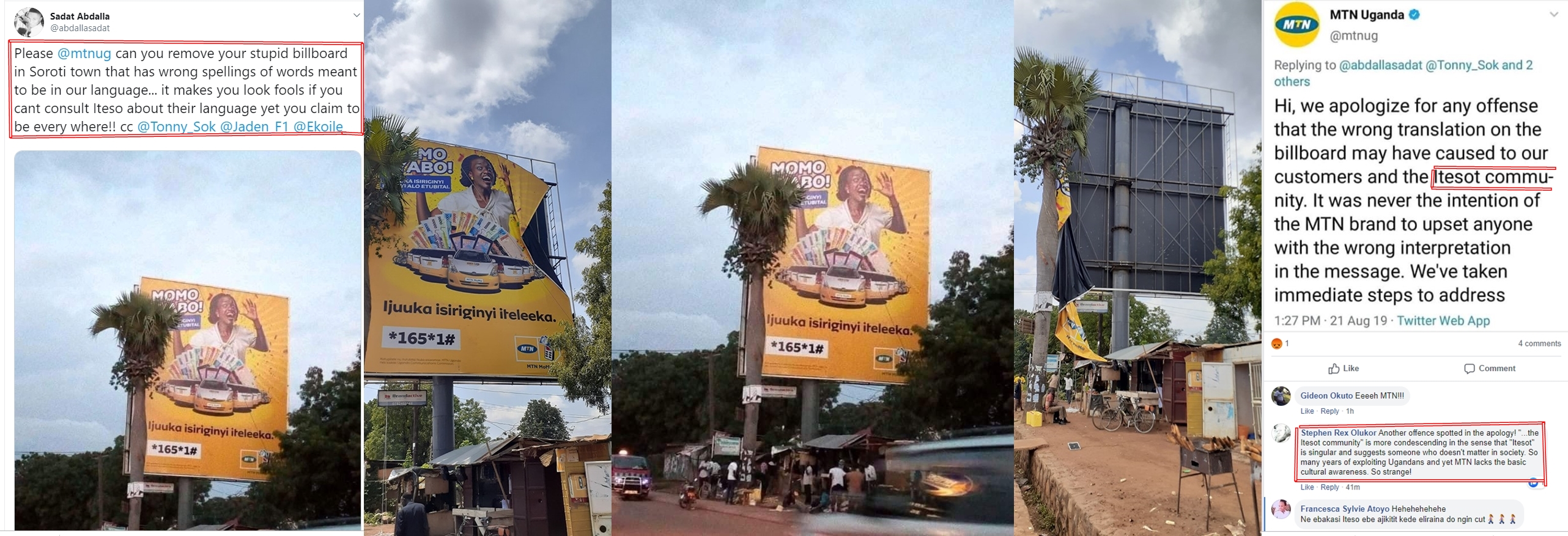
Conjointly with an app, the C-Face Smart mask can transcribe dictation amplify the wearer’s voice, and translate speech into eight different languages. As you’d expect, the mask doesn’t work on its own, its instead relying on a wireless link (Bluetooth) to a smartphone and Donut Robotics’ software. The associated app uses machine learning developed with the help of translation experts and specializes in the Japanese language to handle language translations. Most competitor apps focus on translating to and from English. Donut Robotics CEO Taisuke Ono claims it’s “better than Google API, or other popular technologies” for Japanese.
Donut Robotics first developed the translations software for a robot called Cinnamon but when the pandemic hit, the robot project was put on hold. That’s when the team’s engineers came up with the idea to use their software in a facemask.

The cutouts on the front are vital for breathability, so the smart mask doesn’t offer protection against the corona virus. Instead, it is designed to be worn over a standard face mask, explains Donut Robotics CEO Taisuke Ono. Made of white plastic and silicone, it has an embedded microphone that connects to the wearer’s smartphone via Bluetooth. The system can translate between Japanese and Chinese, Korean, Vietnamese, Indonesian, English, Spanish and French.
The impact of Smart face masks in communication amidst Covid-19 Social distancing rules
The mask’s Bluetooth chip can connect to smartphones up to 32 feet (10 meters) away, says Ono. He hopes the mask will make new social distancing norms in locations including hospitals and offices easier, by enabling good communication.
The future of these new normal smart face masks
The company is expecting to make the mask available from January 2021 at a cost of roughly $38. If you want to take advantage of the translations and dictation features, there’s going to be a monthly charged, but the ongoing cost has yet to be disclosed. It also seems likely this will be the first of many smart masks to appear in the coming months, because companies are now realizing this is a new category of wearable and there’s the potential for millions of customers.
Why your business shouldn’t lag behind in the new normal times – Covid-19 times
Simply take a look why you need language translations services even in the new normal era:
- Due to the pandemic, most businesses have switched to online operation. And so, you need translations for the growth of your online business. Though online businesses generally target a particular group of people of a country sometimes it has been seen that visitors from other countries also visit your website. Language translation services provide a translator medium which translates your website into different languages.
- Hiring language translation services helps you attract a large audience to your business. In business, the products should speak the language but to advertise your products and services and to reach a global audience, you need a medium. Translations will increase your business to an extent you wouldn’t have ever thought.
- There are many companies that need a translation of the technical text. Outsourcing language translation services in Africa helps you concentrate on your business goals and the translation work to be done by the efficient team of translators. You invest a little money and in return, you get to expand your business globally.
- Language translations are specially used in travel and tourism. Translators are required to translate the history of the nation to the tourists visiting the country for vacation.
Language translation services have a huge scope in every field.
- Localization translators have an aim of spreading the product information in different languages and cultures. They possess a high degree of knowledge about the product and the local users of the product. The main aim of the localization translators is to adapt the product information from where it has been manufactured and spread it where it will be actually sold.
- Then there are specialized business translators who translate the information of finance, e-commerce, marketing among others to the dealers from other corners of the world. The aim is to expand the business. They possess great knowledge of business as well as both the languages.
- Medical translators and interpreters promote communication between the hospital management and the patients. Medical translators have strong knowledge of both medical as well as conversational terms in both the languages.
- Conference interpreters generally work in international forums where the people come from all around the world. Conference interpreters are a pro at translating languages into active as well as passive form during this new normal era.
Language translation services in Africa are affordable and provide the best services for the expansion of all types of businesses whether small scale or large scale. Language translations are used everywhere, whether in tourism, business or medical department.
Take no chances!
You can’t afford to lose, adjust to the new normal just like Smart Face mask inventors did! Hire the best language translations services and reach a much wider audience in this new normal era, Covid-19 or Corona times!